GREEN STRATEGIES FOR BUILDING DESIGN
ARC61804
PROJECT 1
PROJECT 1
PASSIVE GREEN BUILDING CASE STUDIES POSTER & BOOKLET
(40% GROUP & INDIVIDUAL)
PROJECT BRIEF
INTRODUCTION
Understanding the local climate and site context is the initial step in maximizing the environmental advantages of a specific location. Effective design should aim for energy efficiency and prioritize the use of sustainable, durable, and high-quality materials to minimize waste.
Key principles of passive design include proper orientation, shading, insulation, natural ventilation, and the use of daylight. The main role of a building is to create an indoor environment that supports its intended function. Therefore, passive design decisions must be guided by how well the building responds to its surrounding context. Essential aspects to consider include site layout and orientation, natural lighting, facade treatment, airflow, thermal insulation, and thoughtful landscaping.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate and critique the implementation of selected passive design strategies across various case studies.
To investigate and interpret the core theories and principles underlying passive green building design strategies.
TASKS
Group Assignment Overview (5 Members)
Choose 2 case studies (3–5 storeys):
-
1 from tropical climate
-
1 from another climate (Arid / Mediterranean / Temperate Continental / Polar)
a) Identify & compare passive design strategies in both cases
-
Site planning
-
Daylighting
-
Façade design
-
Natural ventilation
-
Strategic landscaping
b) Analyse the impact of these strategies on
-
Spatial quality
-
User experience
c) Final deliverables
-
A0 infographic poster
-
A4 landscape booklet (20–25 pages max)
-
Include text, diagrams, sketches, drawings, and images
OUTCOME (BOOKLET)
-
Explain the concept of passive sustainable design, including the green technologies involved and the relevant design strategies that minimize environmental impact through natural, energy-efficient methods.
-
Examine passive design strategies in relation to different climates and cultural settings, and evaluate how they influence spatial quality and the overall experience of building users.


1.0 Discipline Specific Knowledge
3.0 Thinking And Problem Solving Skills
This project strengthened my understanding of passive sustainable design principles and how they are applied in real-world architectural contexts. By analyzing case studies from different climates, I gained deeper insight into how design responds to environmental and cultural factors.
Throughout the project, I developed critical thinking skills by comparing and evaluating different passive strategies based on climate, site, and user needs. Problem-solving was essential in synthesizing complex data into clear visual and written content for the poster and booklet.
REFLECTION
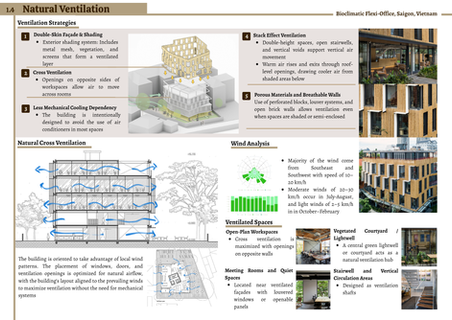
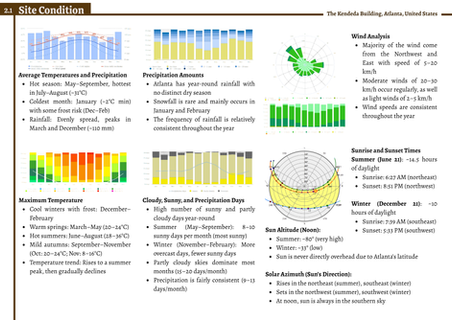
Working on this passive design case study project has been a valuable and eye-opening experience. Through the comparative analysis of the Bioclimatic Flexi-Office and the Kendeda Building, I developed a stronger understanding of how climate and cultural context influence architectural strategies. The project challenged us to go beyond surface-level design elements and to deeply evaluate how passive strategies—such as site planning, daylighting, facade design, natural ventilation, and strategic landscaping—can shape both environmental performance and user comfort.
Collaborating as a team, we each contributed to different aspects of the research and visual presentation, allowing us to merge our strengths and learn from one another. Creating the A0 infographic poster pushed us to simplify complex information into a clear, visual narrative, which helped sharpen both our analytical and design communication skills.
Overall, this project has deepened my appreciation for passive design and has equipped me with practical insights that I can apply in future architectural work. It reinforced the value of designing with climate, culture, and user experience in mind.